Cybersecurity Threats in the Remote Work Era: Strategies for Securing Distributed Workforces
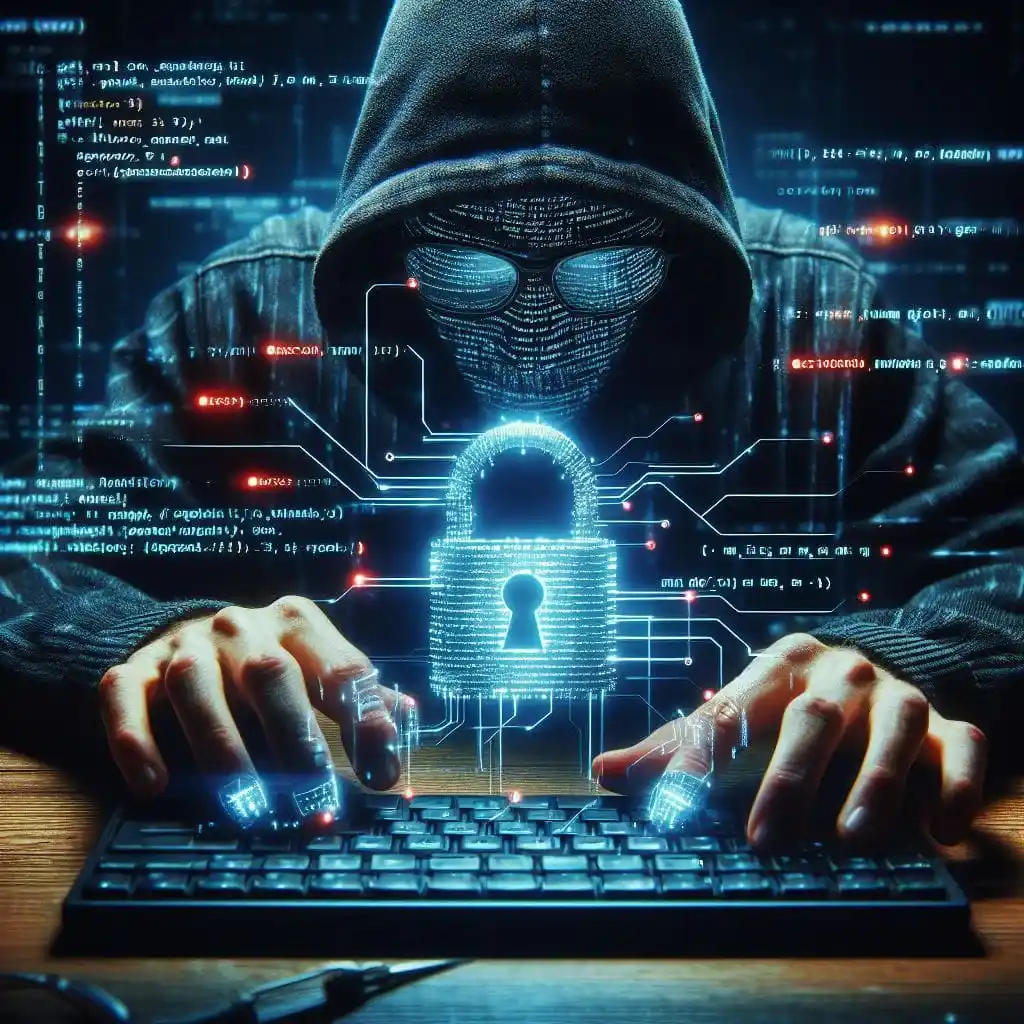

In recent years, the landscape of work has dramatically transformed with the rise of remote work. This shift, accelerated by technological advancements and the global pandemic, has brought about numerous benefits but has also introduced a host of cybersecurity challenges. As organizations adapt to distributed workforces, they must navigate a complex cybersecurity landscape to ensure the protection of sensitive data and assets. This blog will explore the cybersecurity threats remote work environments face and discuss strategies for effectively securing distributed workforces.
The advent of remote work has revolutionized the traditional office model, enabling employees to work from anywhere with an internet connection. While this flexibility offers numerous advantages, it also presents significant cybersecurity risks. Remote employees often access company networks and sensitive data from unsecured devices and networks, making them vulnerable targets for cyber attacks. IT Consulting NJ experts help to secure your business from potential risks.
Common Cybersecurity Threats in Remote Work Environments
a. Phishing Attacks: Phishing remains one of the most prevalent cybersecurity threats, with remote employees being prime targets. Attackers often use deceptive emails, messages, or websites to trick employees into divulging sensitive information or installing malware.
b. Malware and Ransomware: Remote devices are susceptible to malware and ransomware attacks, compromising sensitive data and disrupting business operations. Employees may inadvertently download malicious software from unsecured websites or through phishing attempts, posing a significant threat to organizational security.
c. Insider Threats: The remote work environment can increase the risk of insider threats, where employees intentionally or unintentionally misuse company resources or disclose confidential information. Remote employees may engage in unauthorized activities that compromise data integrity and confidentiality without proper oversight.
d. Weak Authentication Practices: Inadequate authentication practices, such as weak passwords or the reuse of credentials, can pose significant security risks in remote work environments. Attackers may exploit these vulnerabilities to gain unauthorized access to corporate networks and systems, leading to data breaches and other security incidents.
Cybersecurity Strategies for Securing Distributed Workforces
Implementing Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
By requesting various forms of verification from users before granting access to corporate systems or data, multi-factor authentication offers an additional layer of security. By implementing MFA, organizations can mitigate the risk of unauthorized access and enhance overall security posture. If you want to implement multi-factor authentication, consult with IT Support New York professionals.
Conducting Regular Security Awareness Training
Educating remote employees about cybersecurity best practices is crucial for mitigating risks and reducing the likelihood of security incidents. Organizations should provide comprehensive security awareness training to remote workers, covering topics such as phishing awareness, password security, and safe browsing habits.
Enforcing Endpoint Security Measures
Endpoint security solutions, such as antivirus software and endpoint detection and response (EDR) tools, help protect remote devices from malware and other threats. By deploying robust endpoint security measures, organizations can detect and respond to security incidents in real-time, safeguarding remote endpoints and sensitive data.
Implementing Zero Trust Architecture
Zero Trust Architecture is a security model based on the principle of “never trust, always verify.” Organizations can establish strict access controls and granular user permissions by adopting a Zero Trust approach, minimizing the risk of unauthorized access and lateral movement within the network.
Securing Remote Access Technologies
Remote access technologies, such as virtual private networks (VPNs) and remote desktop protocols (RDP), play a crucial role in enabling remote work. However, these technologies can also introduce security vulnerabilities if not properly configured and secured. Organizations should implement robust security controls, such as encryption and access controls, to protect remote access channels from unauthorized access and data breaches.
Best Practices for Securing Remote Work Environments
Regularly Update Software and Systems
Keeping software and systems up to date is essential for addressing security vulnerabilities and mitigating the risk of exploitation by cyber attackers. Organizations should implement patch management processes to ensure timely updates and patches are applied to remote devices and systems.
Secure Data Transmission
Encrypting data in transit helps protect sensitive information from interception and unauthorized access. Organizations should use secure communication protocols, such as Transport Layer Security (TLS) and Secure Shell (SSH), to encrypt data transmitted between remote devices and corporate networks.
Monitor and Audit Remote Access Activities
Continuous monitoring and auditing of remote access activities enable organizations to detect and respond to security incidents in real-time. By monitoring user activity, network traffic, and system logs, organizations can identify anomalous behavior indicative of potential security threats and take appropriate action to mitigate risks.
Develop an Incident Response Plan
In the event of a security incident, organizations must have a comprehensive incident response plan in place to respond to and mitigate the impact of the incident effectively. The incident response plan should outline roles and responsibilities, escalation procedures, and communication protocols to ensure a coordinated and timely response to security incidents.
Conclusion
As remote work continues to become the new norm, organizations must prioritize cybersecurity to protect sensitive data and assets from evolving threats. By implementing robust security measures and best practices, organizations can secure distributed workforces effectively and mitigate the risks associated with remote work environments. With a proactive approach to cybersecurity, organizations can enable remote work while maintaining the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of critical business resources.
In conclusion, the remote work era presents both opportunities and challenges for organizations seeking to adapt to the evolving demands of the modern workforce. By understanding the cybersecurity threats associated with remote work environments and implementing effective security strategies and best practices, organizations can secure distributed workforces and safeguard against potential threats. As remote work continues to reshape the future of work, cybersecurity will remain a critical priority for organizations striving to maintain a secure and resilient infrastructure in an increasingly digital world.